Short Breaks
SCOPE OF THIS CHAPTER
This chapter takes account of:
- Care Planning, Placement and Case Review (England) Regulations 2010;
- The Children Act 1989 Guidance and Regulations - Volume 2: Care Planning, Placement and Case Review (2015);
- The Breaks for Carers of Disabled Children Regulations 2010; and
- Carers and Disabled Children Act 2000;
- Short Breaks for Carers of Disabled Children;
- Short Breaks Statutory Guidance 2010;
- Children and Families Act 2014.
RELATED CHAPTERS
Placements in Other Arrangements Procedure
AMENDMENT
In September 2021, information was added in to Section 7, Short Break Settings, in relation to the prohibition on looked after children under the age of 16 being placed in 'other arrangements' placements for the purposes of a short break.1. The Legal Basis for Short Breaks
Children may be provided with short breaks under the following legislation:
Section 17
Under Section 17 Children Act 1989, in which case they are not looked after children, the 2010 Regulations do not apply and there is no requirement to appoint an Independent Reviewing Officer (IRO). A Child in Need Plan is required in accordance with the Assessment Framework. Reviews should be carried out at least every 6 months and more often if required.
Under Section 20 Children Act 1989, where the short breaks exceed a total of 17 days per placement/75 days per 12-month period and/or take place in more than one setting. In these circumstances, the child is looked after, an IRO must be appointed and a Care Plan drawn up. The 2010 Regulations apply in full, including the provisions on frequency of Looked After Reviews (see Section 5, Reviews) and Social Work Visits (see Section 6, Social Work Visits).
The legal basis on which services are provided should be clear. The decision to provide a short break under Section 17 or under Section 20 should be informed by the assessment of the child's needs and should take account of parenting capacity and wider family and environmental factors, the wishes and feelings of the child and his/her parents and the nature of the service to be provided.
The key question to ask in deciding whether to provide the short break provision under Section 17 or Section 20 is how to promote and safeguard the welfare of the child most effectively.
2. Assessment of Needs
Before making, and when reviewing, a decision about whether to provide accommodation under Section 17 or Section 20, there should be a careful assessment of the child and family's needs that addresses:
- Particular vulnerabilities of the child, including communication method;
- Parenting capacity of the parents within their family and environmental context;
- The length of time away from home and the frequency of such stays - the less time the child spends away from home, the more likely it is to be appropriate to provide the accommodation under Section 17;
- Whether short breaks are to be provided in more than one place - where the child has substantial packages of short breaks in different settings, it is more likely to be provided under Section 20;
- Potential impact on the child's place in the family and on primary attachments;
- Observation of the child (especially children who do not communicate verbally) during or immediately after the break by a person familiar with the mood and behaviour of the child (e.g. parents or school staff);
- Views of the child and parents - some children and parents may be reassured by and in favour of the status of a looked after child, while others may resent the implications and associations of the 'looked after' status;
- Extent of contact between short break carers and family and between the child and family during the placement;
- Distance from home; and
- The need for an Independent Reviewing Officer (IRO) to monitor the child's case and to chair reviews.
It is more likely that the arrangements come within Section 20 where families have limited resources and may have difficulties providing support to their child while (s)he is away from home or monitoring the quality of care.
3. Levels of Assessment
3.1 Assessment
An Assessment is required where the trigger for the assessment is a request for a short break, relative need.
For relatively low levels of short break provision, an authority may not need to prepare its own assessment for disabled children who have been assessed through other processes, for example, access to existing local health or educational facilities, receipt of higher level Disability Living Allowance, or locally agreed criteria.
The Children with Disabilities Service has an Early Help model which complements Early Help services available in the Access and Referral Hub. The model is based on LCSB guidance and includes the following structure.
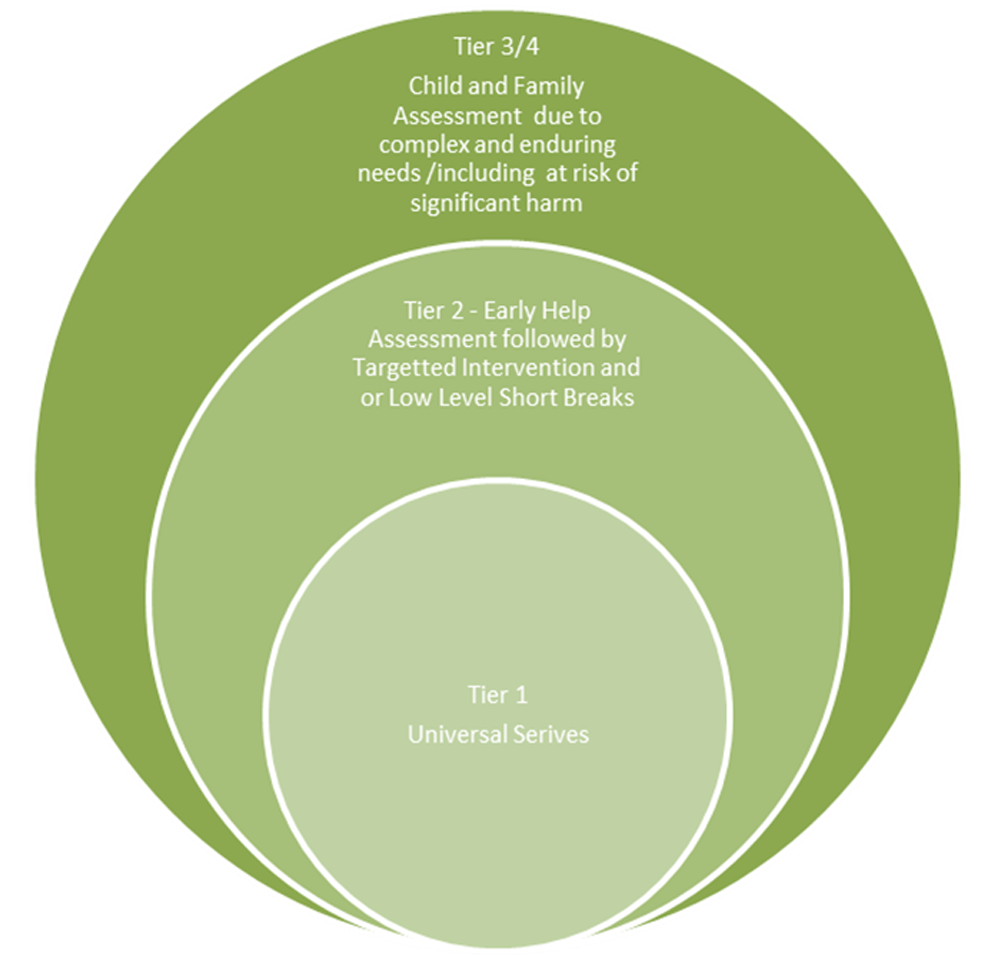
Level 1 Universal Services
- Children's needs at this level are met by universally accessible service e.g. schools, colleges, early years settings, health visiting, children's centres. Children at this level do not need to be referred to Early Help or Children's Social Care.
Level 2 Intervention – Early Help Services - Social Work Assistant
Disabled children and young people who 'meet the threshold criteria for a service' can receive the following interventions:
- Early intervention and childcare;
- Family learning and access to work;
- Positive activities for children and young people which promote their aspirations, health and well being;
- Parenting Programme and Family Support – 'targeted intervention';
- Healthy lifestyles and risky behaviours;
- Emotional well being and counselling support services;
- Low level carer breaks.
The process will require an Early Help Assessment and recommendation to the Manager. If appropriate an Early Help package will be considered at the weekly Children with Disabilities Allocation Panel (CDAP) and then an Early Help Plan or Short Break Plan monitored and reviewed through Team Around the Child Meetings (minimum 6 monthly). This will contribute to the process to develop an Education, Health & Care Plan involving colleague in education and health.
Level 3 & 4 Intervention – Children in Need or with urgent, immediate or other high priority needs including CP and LAC
Disabled children and young people who 'meet the threshold criteria for a service' and whose needs are complex, enduring, and cross many domains will often be at risk of isolation, family breakdown, lack of good enough or consistent and confident parenting, significant harm or of coming into care.
Additional risks may include barriers to development and the minimising of hopes, aspirations and potential. When undertaking an assessment of a disabled child, the local authority must also consider whether it is necessary to provide support under Section 2 of Chronically Sick and Disabled Persons Act (1970).
Children with disabilities with these high level needs will require a Child and Family Assessment which is then updated at least every 12 months as part of a Short Break Plan or other planning documentation if subject a Child Protection Plan or Looked After. Children and families are supported by a combination of universal, targeted and specialist services and coordinated by a Social Worker.
Depending on the severity of need this may include:
- Social Work Assessments (C&FA);
- Child In Need planning and review;
- Short-break planning including overnight respite;
- Family Group Meetings and Conferences;
- Parenting Programme and Family Support – 'targeted intervention';
- Complex Multi-Agency meetings;
- Child in need of Protection planning and review;
- Children in need of care planning and review.
The services to be provided to the child and family will be agreed at either Children with Disabilities Panel (CDAP) or the Joint Agency Panel (JAP). The latter is held monthly and the membership includes representation from Education, Integrated Care Board, CAMH (Main and Specialist Learning Disability), CBC Commissioning. Both panels are chaired by the Head of Service for Children with Disabilities providing management oversight of the cases and the processes.
Senior Practitioner Role
The Teams Senior Practitioner would be subject to the same social work process at Level 3/4 with the addition of:
- Protected caseload of complex cases;
- Leadership in case management;
- Leadership in research based practice / reflective practice issues / group;
- Supervision of Early Help workers and processes as required;
- Support the managers in monitoring an improving performance;
- Overseeing duty and making delegated decisions.
3.2 Carer's Assessment
Parent Carer's have rights to stand-alone assessments under the Children and Families Act 2014.
Section 97 of the Children & Families Act 2014 requires local authorities to assess parent carers on the appearance of need or where an assessment is requested by the parent.
This is called a "Parent Carers Needs Assessment".
Where requested, then the local authority must assess whether that parent has needs for support and, if so, what those needs are. The assessment must include an assessment of whether it is appropriate for the parent to provide, or continue to provide, care for the disabled child, in the light of the parent's needs for support, other needs and wishes.
The assessment must also have regard to:
- The well-being of the parent carer; and
- The need to safeguard and promote the welfare of the child and any other child for whom the parent carer has parental responsibility.
Following assessment, the local authority must then decide:
- Whether the parent has needs for support;
- Whether the child has needs for support;
- And if so whether those needs could be met (wholly or partly) by services under Children Act 1989, Section17.
4. Plans
4.1 Short Break
This is applicable where short breaks are provided under Section 17 Children Act 1989.
The Short Break Plan should be in writing and set out clearly all the services that are to be provided to meet the child's needs. Many families with disabled children receive a range of services to meet their child's needs. Wherever possible there should be a single plan which includes the full range of family support services on a multi-agency basis. The plan will show how the short break will meet the needs of the child and family identified in the assessment. It will:
- Have clear and realistic objectives;
- Include the ascertainable wishes and feelings of the child and views of the family;
- Follow consideration of options, including but not limited to direct payments;
- State the nature and frequency of services, as far as is practicable, including health and social care in the same plan, especially if short breaks are provided from different agencies;
- State the child's health, emotional and behavioural development including full details about any disabilities and clinical needs the child may have and medications they may require;
- State the child's specific communication needs, especially for children who communicate non-verbally, and include the child's likes and dislikes with particular regard to leisure activities;
- Desired outcomes to evidence aspirations;
- Include the results of all necessary risk assessments which could include, depending on the child's impairment, moving and handling, invasive procedures, and behaviour;
- State contact arrangements for emergencies;
- State commitments of professionals involved;
- Refer to or summarise any other important documents about the child's development;
- Confirm those caring for the child have been selected following the advice set out in Government guidance on direct payments; and
- Outline arrangements to review the plan.
The plan should include all the information necessary to ensure the welfare of the child in the short break. Much information may already be available from a variety of sources including the parent-held child record. The plan should be made available as necessary in accessible formats.
The Short Break Care Plan must set out the arrangements to meet the child's needs with particular regard to:
- The child's health and emotional and behavioural development, any disability, medical needs and medications;
- The child's specific communication needs;
- Promoting contact with parents/anyone with Parental Responsibility;
- Arrangements for contacting parents as necessary, in particular an emergency contact number;
- The child's likes and dislikes regarding stimulation and leisure interests;
- How the carers, as appropriate, promote the child's educational and leisure achievement;
- The name and address of the registered medical practitioner;
- The type of accommodation, address, name of person responsible;
- The child's personal history, religious persuasion, cultural and linguistic background and racial origin;
- The respective responsibilities of the local authority and parents/anyone with Parental Responsibility; any delegation of responsibility from parents to the local authority; the respective roles and responsibilities of the placement provider, Social Worker, Independent Reviewing Officer (IRO) and other staff employed or commissioned by the local authority to contribute to the plan for the child's care; the respective safeguarding responsibilities of the provider and the local authority;
- The expected duration of the arrangements and the steps to end them; arrangements for giving notice of intention to terminate the placement along with the local authority's responsibilities for convening a review of the child's Care and Pathway Plan where there is a risk of the placement being terminated;
- Frequency of visits;
- Financial arrangements for the placement;
- When the child is placed with a local authority-approved foster carer, confirmation of the foster carer's agreement;
- The provider's responsibilities for notifying the child's Social Worker of any significant change in the child's circumstances.
As far as practicable, the child should be involved in agreeing the Plan.
The parents must be fully involved in all aspects of agreeing the Short Break Care Plan.
The plan should be signed by the parents, the local authority, those providing the care / the provider agency and, where appropriate, the child.
There is not a requirement for a separate Placement Plan for short breaks.
5. Reviews
5.1 Reviews - All Cases
No significant change to a Child in Need Plan or a Short Break Care Plan should be made unless it has first been considered at a review or agreed allocation panel.
In each case, whether children are provided with accommodation under Section 17 or under Section 20, the review should consider whether this continues to be the most appropriate legislative basis for the service provided.
A record should be kept, recording the views of those involved in the review, decisions taken and the identity of the persons responsible for implementing them.
5.2 Children in receipt of Short Breaks under Section 17 Children Act 1989 (Situation 1)
A case review for a child who is not looked after should:
- Ensure the service(s) provided meet the needs identified in the Child in Need Plan and safeguard and promote the welfare of the child;
- Focus on outcomes for the child and family;
- Be a multi-agency review whenever possible. Different elements of a child's care package should not require a separate review;
- Include the ascertainable wishes and feelings of the child and the views of the family;
- Take place at least six monthly. The needs of the child and family may indicate that a review should take place before the statutory minimum, for example if the child's condition is changing quickly, or there are changed family circumstances, or where there is a complex package of services including direct payments.
A review will usually include a face to face meeting but in some cases, regular review meetings may not be necessary. Generally it should be possible to include a review of short breaks with a review of other aspects of a child's health, education or development, where some of the same people will already be together.
Reviews should take the form of a meeting when requested by the family. In all circumstances a face to face meeting should take place at least six monthly.
Having an advocate may be particularly useful for disabled young people moving towards adulthood.
5.3 Children in receipt of Short Breaks under Section 20 Children Act 1989 (Under a Series of Short Breaks)
Reviews are less frequent than for looked after children in Situation 3:
- The first review must take place within 3 months of the start of the first placement;
- Second and subsequent reviews must take place at intervals of not more than 6 months;
- Reviews may be convened earlier, e.g. at the request of the child, parents or carer; or in cases where the child is particularly vulnerable; or where the child is provided with a high level of short breaks.
5.4 Children in receipt of Short Breaks under Section 20 Children Act 1989 (Who Are Looked After)
The 2010 Regulations in relation to Looked After Reviews apply in full, and reviews will take place as follows:
- The first review must take place within 20 working days of the first placement;
- The second review must take place not more than 3 months after the first;
- Subsequent reviews must take place at intervals of not more than 6 months.
For further details, see the Looked After Reviews Procedure.
6. Social Work Visits
Visits should usually be undertaken by either a qualified Social Worker or social work assistant and always by a person with the skills and experience to communicate effectively with the child and fulfil the functions of the visit.
Section 17
Visits should take place at least six monthly or as agreed at supervision by the Manager / Supervisor.
Section 20 (Short Breaks)
Visits should take place at regular intervals to be agreed with the Independent Reviewing Officer and parents/person(s) with Parental Responsibility and recorded in the Short Break Care Plan before the start of the first placement.
In any event:
- The first visit must take place within 3 months of the first placement day or as soon as practicable thereafter;
- Subsequent visits must take place at intervals of no more than 6 months for as long as the short breaks continue.
Section 20 (LAC)
See also Part 5, Looked After Children Procedures.
- Within one week of the start of the placement;
- Thereafter, at intervals of no more than six weeks for the first year.
7. Short Break Settings
Following the assessment of the child and family, short breaks can be arranged in a number of settings which are subject to different registration and inspection requirements.
| Outline Requirements on Settings Where Short Breaks Might Take Place | ||
| Hospices | Regulated by the Care Quality Commission (CQC) under the Care Quality Commission (Registration) Requirements 2009. | Guidance about compliance with the registration requirements was issued by CQC in December 2009. Regulations for Service Providers and Managers. |
| Local authority foster care | Fostering services are registered with and inspected by Ofsted. | Revised National Minimum Standards which came into force in April 2011. |
| Children's homes | Children's homes are registered with and inspected by Ofsted. | Quality Care Standards for children's homes. |
| Residential special schools | Different regimes apply depending on whether the residential special school is maintained, non-maintained or independent. | The National Minimum Standards for residential special schools are under review. |
Looked after children under the age of 16 cannot be placed in 'other arrangements' placements for the purposes of a short break except where the accommodation is provided as part of a residential holiday scheme for disabled children or is one of the other exempted regulated settings under Regulation 27A Care Planning, Placement and Case Review (England) Regulations 2010:
- A care home as defined in section 105(1) Children Act 1989;
- A hospital as defined in section 275(1) of the National Health Service Act 2006;
- A residential family centre as defined in section 4(2) of the Care Standards Act;
- A school within the meaning of section 4 of the Education Act 1996 providing accommodation that is not registered as a children's home as defined in section 105(1) Children Act 1989.
Further detail on short break provision can be found in the Central Bedfordshire Short Breaks Statement.
8. Providing Care in the Child's own Home
The key to providing safe care to children in their own homes is the same as to the provision of safe care elsewhere. It is essential that safe recruitment practices are followed and staff are properly trained and supervised and that the requirements of the Vetting and Barring Scheme are complied with.
Where the local authority provides a sitter or overnight carer in the child's own home, the child is not being provided with accommodation by the local authority and the authority is therefore providing the short break service under Section 17 Children Act 1989.
However, caring for or supervising children unsupervised, or providing Personal Care to them, will come within the definition of Regulated Activity under the Safeguarding Vulnerable Groups Act 2006 as amended by the Protection of Freedoms Act 2012 and the requirements of the Disclosure and Barring Service in relation to regulated activities will apply.
Best practice is that the child should be cared for by an approved local authority foster carer. Childminders with whom the local authority places or wishes to place children overnight (or childminders wishing to take on such work) should be asked to apply for approval as local authority foster carers. It is not appropriate for the local authority to provide overnight accommodation with childminders who are not also approved foster carers.
9. Providing Care in the Carer's own Home or in the Community
It is essential that individuals providing care in their own homes are subject to full employment and personal checks, as well as safe recruitment methods, and that they are provided with induction and training.
There are no requirements for agencies to register with Ofsted or the Care Quality Commission if they provide services to support disabled children in the community or in their own homes, unless they provide Personal Care. If Personal Care is provided, services must register with the Care Quality Commission and comply with the relevant standards, and the activities will be Regulated Activity.
